Describe the Structure of a Typical Bacterial Cell
By Biology experts to help you in doubts scoring excellent marks in Class 11 exams. An outer cell wall and an inner cell membrane.
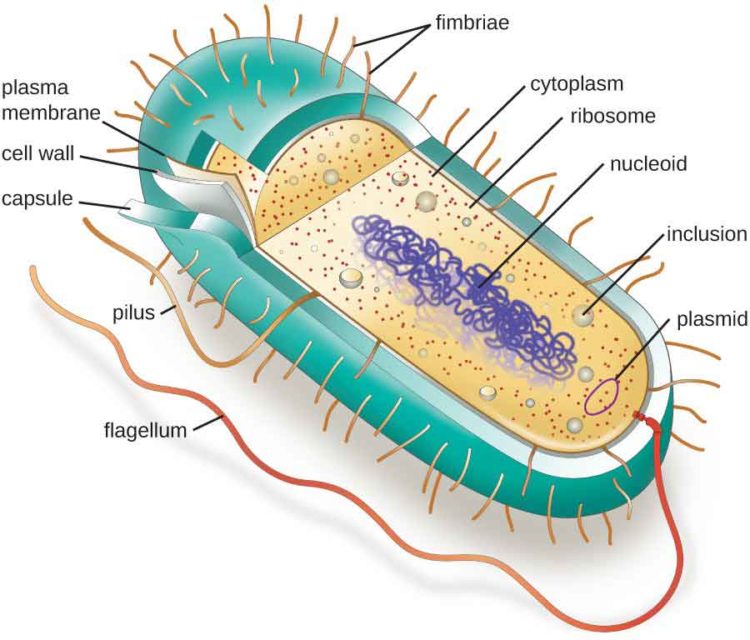
Bacterial Cell Structure And Function Pharmapproach Com
Bacterial cells are generally surrounded by two protective coverings.
. The cocci are round the bacilli are rods and the spirochetes are spiral-shaped. 2 Compare and contrast gram-positive gram-negative and Acid Fast cell envelopes with regards to structure and chemical composition 3 Describe the Gram stain procedure 4 List the 3 components of bacterial cell envelopes that are highly toxic to mammalian cells. 1 List the three parts of bacterial taxonomy.
The 70S ribosome is made up of a 50S and 30S subunits. Bacterial morphology is determined by the cell wall. Start your trial now.
Capsule is 98 water and 2. Coccus-shaped bacteria are seen as single cells pairs long chains or clusters whereas rod-shaped bacteria are simply cells that are longer in one dimension than the other resulting in fat thin short or long rods. Hence they are classified as prokaryotic organisms.
All prokaryotes have 70S where S Svedberg units ribosomes while eukaryotes contain larger 80S ribosomes in their cytosol. It is 15-20 nm hair like helical structure emerges from cell wall. For example L-forms of the rod-shaped bacterium Bacillus subtilis appear round when viewed by.
Bacteria are classified by shape into three basic groups. Bacteria are all single-celled. And a cytoplasmic region that contains the cell chromosome DNA and ribosomes and various sorts of inclusions Figure 1.
Typical L-form cells are spheres or spheroids. It is the outer covering of protoplasm of bacterial cell. Distinguish a typical bacteria cell from a typical plant or animal cell terms of cell shapes arrangements size and cell structures.
Appendages attachments to the cell surface in the form of flagella and pili or fimbriae. The shape of a bacterium is determined by its rigid cell wall. Such organisms are called extremophiles.
Weve got the study and writing resources you need for your assignments. Outer most layer of bacteria. Plasmids play a key role in antibiotic resistance.
Bacteria being prokaryotic in nature are much simpler in comparison to the animal cells. Cocci bacilli and spirochetes Figure 21. Certain bacteria like mycoplasmas have no cell wall at all.
A an extensive endoplasmic reticulum. Larger bacterial cells may be. Flagellum refer to thread-like structures attached to the surface of some bacteria.
Bacterial Cell Wall Peptidoglycan murein rigid structure that lies just outside the cell plasma membrane two types based on Gram stain Gram-positive. Bacterial cell Structure and Function 1. The cells are all prokaryotic.
Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms with the absence of the nucleus and other c ell organelles. Capsule is 02µm thick viscus layer outer layer to the cell wall. A cell envelope consisting of a capsule cell wall and plasma membrane.
They are made up of repeating units of a simple protein called flagellin. In addition to this they have three distinct characteristic features namely. This means they do not have a nucleus or any other structures which are surrounded by membranes.
The structure of bacteria is known for its simple body design. This diagram illustrates the structure of a typical bacterial cell showing the cell wall cell envelope chromosome and a plasmid. It is made of peptidoglycon and it protects cells against osmotic shock most important and physical damage 2.
Flagella are approximately 001 µm in diameter and 15 µm in length. First week only 499. Solution for Describe the structure of a typical bacterial RNA polymerase holoenzyme.
Since the L-form has no cell wall its morphology is different from that of the strain of bacteria from which it is derived. SHAPE SIZE OF BACTERIA. Terms in this set 73 Bacteria cell structure.
Determined by plane of division and by separation or not. Spirillum-shaped bacteria are curved rods. Some bacteria are variable in shape and are said to be pleomorphic many-shaped.
Stain pink or red. Some bacteria may even have a third outer protective layer called a capsule. Step by step text solution for Describe the structure of a typical bacterial cell with the help of well labelled diagram.
Thin peptidoglycan and outer membrane. Cocci and rods most common and various others. Nevertheless bacteria do possess a rather complex surface structure having a.
A typical bacterial cell contains the following structures. They enable bacteria to move and cells lacking flagella are nonmotile. The following points highlight the seven important components of bacterial cell.
Structurally there are three architectural regions. In most bacteria the most numerous intracellular structure is the ribosome the site of protein synthesis in all living organisms. The whip-like extensions often cover the surfaces of bacteria the long ones called flagella or the short ones.
It is imm View the full answer. They are also very versatile organisms surviving in extremely inhospitable conditions. B essentially lack a membrane-bound nucleus.
A plasmid can undergo rapid genetic changes.
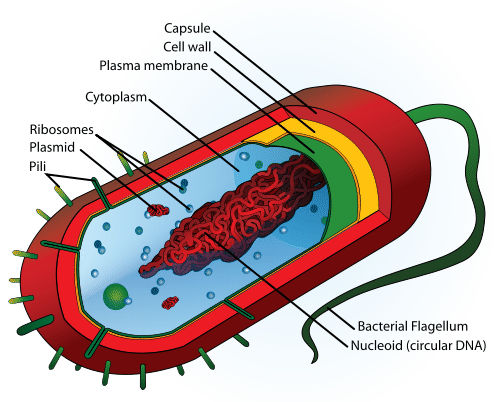
Bacteria Characteristics Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation

The Schematic Diagram Of Bacterial Cell Structure Download Scientific Diagram
No comments for "Describe the Structure of a Typical Bacterial Cell"
Post a Comment